Request More Information
Protein Sequencer
Edman Degradation

Advancements in medicine have made biopharmaceuticals highly effective, low in side effects, and can be used to treat a wide range of illnesses. However, biopharmaceutical production comprises multiple processes including manufacture, refinement, dosage form design, and storage. In order to guarantee the quality of biomedicines, influences originating from raw materials and manufacturing processes need to be taken into consideration in addition to performing qualification testing of products. This means that management of manufacturing and quality of drugs requires a different approach compared to chemical synthesized low molecular drug products. Guidelines currently exist for evaluating the quality of biomedicines requiring that characteristic analyses are performed to determine identity, and one type of characteristic analysis is N-terminal amino acid sequencing. This analysis is performed to compare and verify the N-terminal amino acid sequence presumed from the gene sequence with the N-terminal amino acid sequence of the biomedicine product. The analysis technique used is the Edman method. This technique determines amino sequences by cleaving amino acids sequentially from the N-terminus of proteins and obtains very reliable amino acid sequences. The PPSQTM- 51A/53A Protein Sequencer is a system that automates this technique. This system facilitates identification of amino sequences from the N-terminus of target proteins and peptides.
While amino acid sequences being analyzed by mass spectrometry has become commonplace, the use of a protein sequencer does have its advantages. While providing secondary confirmation to mass spec analysis, protein sequencers also could prove advantageous in the biosimilars market for sequence confirmation. Protein sequencers are highly reliable in providing results and easy to operate, making them an essential tool for any lab. Our PPSQ system combines an Edman reaction section with an HPLC, cleaving your peptides via Edman degradation and derivatizing to inject onto HPLC. The PPSQ also has the capability to run on an isocratic or gradient system, as well as processing software that provides compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 11 guidelines.

Gradient System
-

Fig. 1 Protocol for N-Terminal Amino Acid Sequencing
-

Fig. 2 PVDF Membrane After Electroblotting
Featured Applications
Analysis of Long-Chain Amino Acid Sequences Using a Protein Sequencer—Gradient System —
Once samples are applied to the membrane, analysis using the protein sequencer is almost completely automatic and requires no additional time or trouble. By using protein sequencer data to supplement information obtained with a mass spectrometer, which is currently the most common method, even more reliable information can be obtained about amino acid sequences in proteins and peptides.
Analysis of Long-Chain Amino Acid Sequences Using a Protein Sequencer — Isocratic System —
Biopharmaceuticals are drugs produced using living organisms,such as microbes or cell cultures. Unlike small-molecule drugs manufactured by chemical synthesis, incubation during biopharmaceutical manufacturing can be impacted by a variety of factors, so even slight changes can affect the final products. Therefore, to maintain the safety and efficacy of biopharmaceuticals, the manufacturing processes must be strictly controlled. N-terminal amino acid sequences are typically analyzed for characterization analysis, which is one such quality control technique. Using a protein sequencer for that analysis can ensure highly reliable amino acid sequencing results. Therefore, a protein sequencer is not only useful for research and development applications but can also be very useful for quality control applications.
Detection of Reductively-Alkylated Cysteines Using Protein Sequencer
This article introduces an example of identification of a PTH-modified cysteine (phenylthiohydantoin derivative of reductively-alkylated cysteine) by analyzing reductively-alkylated peptides/proteins with PPSQ™ -50A series protein sequencer systems (isocratic system and gradient system).
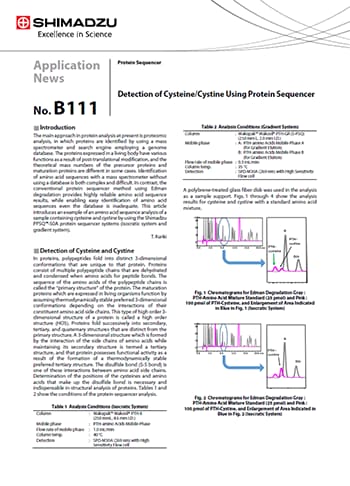
Detection of Cysteine/Cystine Using Protein Sequencer
The PPSQ-50A protein sequencer system enables easy and accurate identification of N-terminal amino acid sequences and can also identify cysteine and cystine. Because cysteine and cystine are degraded more markedly than other amino acids during Edman degradation, a certain sample amount is necessary in order to determine the elution position with a protein sequencer. In the future, this Shimadzu protein sequencer system is expected to be an effective tool for structural analysis in proteomic analysis and evaluation of these substances as synthetic intermediates before they form disulfide bonds during peptide synthesis.
Improving the Yield of Basic Amino Acids in a Protein Sequencer
Although the improved sequencing protocol caused a slight increase in background noise in chromatograms due to the products of Edman degradation, this increase had no impact on identification of PTH-amino acids, and the results confirmed an improved percent yield of basic amino acids. Based on the above findings, the improved protocol seems effective at improving basic amino acid yields from Edman degradation.
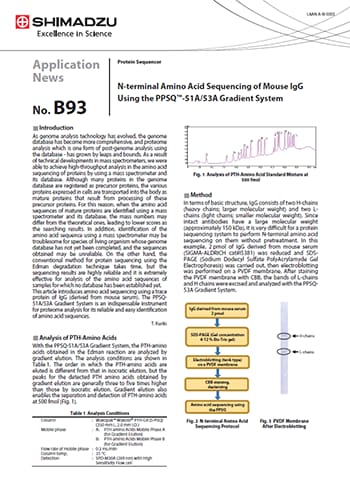
N-terminal Amino Acid Sequencing of Mouse IgG Using the PPSQ™-51A/53A Gradient System
This article introduces amino acid sequencing using a trace protein of IgG (derived from mouse serum). The PPSQ-51A/53A Gradient System is an indispensable instrument for proteome analysis for its reliable and easy identification of amino acid sequences.
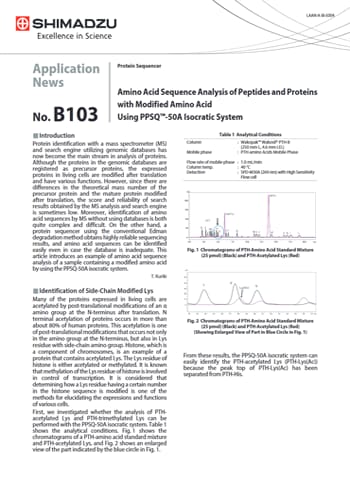
Amino Acid Sequence Analysis of Peptides and Proteinswith Modified Amino Acid Using PPSQ™-50A Isocratic System
The PPSQ-50A isocratic system enables easy and accurate identification of N-terminal sequences and can also identify modified amino acids. Thus, this can be considered an effective system as a tool for identification of post-translational modifications in protein analyses.
Shimadzu Protein Sequencer PPSQ-51A/53A-Compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 11
LabSolutions PPSQ software provides compliance with FDA 21 CFR Part 11 guidelines and enables compliance with the security, user management, and audit trail requirements specified by FDA 21 CFR Part 11.
Related Products
News / Events
-
AAPS Pharm Sci 360 2025
November 9-12
Henry B. Gonzalez Convention Center
San Antonio, TX -
Pharma Community Network Event
Shimadzu Scientific Instruments and ZefSci invite you and your analytical teams to a pharma community networking event to celebrate 150 years of science and innovation at The Foundry & Lux in South San Francisco. Our event will be built around innovation, collaboration, and connection.
-
ASMS (American Society for Mass Spectrometry) 2025
June 1-5
Baltimore Convention Center
Baltimore, MD -
Shimadzu Scientific Instruments Opens Boston Location of Its R&D Center Focus will be on promoting customer-oriented development to expand business in the pharmaceutical field
Shimadzu Scientific Instruments, Inc. (SSI, Columbia, Maryland, USA), a Shimadzu Group company, has opened a satellite lab in Boston, Massachusetts to be the base of its collaborative research and development activities on the East Coast. Established to conduct research and development more closely linked to customers, SSI's R&D Center consists of three bases, with the main facilities at its Maryland headquarters, a West Coast location, and this new space in Boston near the city center. The Boston lab was set up by partnering with Labshares, a shared laboratory service provider for life science companies.